Class documentation of Concepts
Classes | |
| class | Alpha |
| class | Euler |
| class | LimitingEuler |
| class | LimitingTvdRK2 |
| class | Newmark |
| class | Nystroem |
| class | RungeKutta2 |
| class | RungeKutta4 |
| class | Theta |
| class | TimeLinearForm |
| class | TimeStepping |
| class | TimeStepStrategy |
| class | TimeVector |
| class | TvdRK2 |
Detailed Description
Timestepping methods used to solve PDEs in time and space. The discretisation in space is done by the others parts of the library, the discretisation in time is done by this part of the library.
// Space Line msh; concepts::BoundaryConditions bc; linearFEM::Linear1d spc(msh, 4, bc.get()); // Space operators Laplace stiff_bf; concepts::SparseMatrix<Real> stiff(spc, stiff_bf); Identity mass_bf(gauss_p); concepts::SparseMatrix<Real> mass(spc, mass_bf); // Zero initial conditions concepts::Vector<Real> initial(spc) concepts::Vector<Real> d_dt_initial(spc) // External driver Sin_tlf driver_tlf(1.0, 1.0 , 0.0, 0.0, 1); timestepping::TimeVector driver(spc, driver_tlf); // Strategy and Solver timestepping::Newmark timeStepStrategy(mass, stiff, driver, initial, d_dt_initial, 0.01); concepts::SuperLUFabric<> fabric; timestepping::TimeStepping solver(timeStepStrategy, fabric); // Write solutions to file in Gnuplot format for(uint n = 0; n <= 5; ++n) { solver(sol, n*100/5); std::strstream filename; filename << "gnuplot/sol1d-" << n << ".gnuplot" << std::ends; graphics::DataGnuplot(spc, filename.str(), sol); }
The follwing picture illustrates the wave equation solved on a rope.
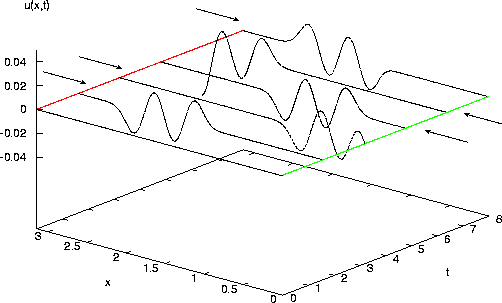
The red line indicates Neumann boundary conditions and the green line Dirichlet boundary conditions. The arrows point in the direction of the movent of the waves. One can clearly see the the waves are reflected on the boundaries and that they do change sign on the Dirichlet boundary and do not change sign on the Neumann boundary.
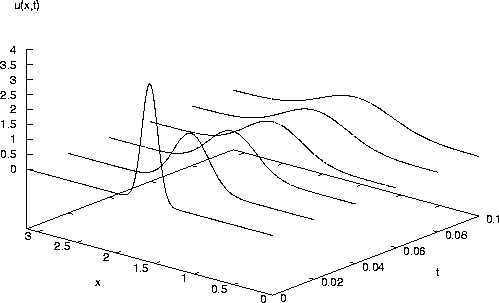
The next picture illustrates the heat equation solved on a wand: the intial peak flattens out as the heat dissipates. Boundary conditions are homogenous Dirichlet.
Generated on Wed Sep 13 2023 21:06:59 for Concepts by
